Remifentanil for postoperative analgesia in patients with myasthenia gravis after video-assisted thoracoscopic thymectomy.
DOI: 10.36210/BerMedJ/epub2222022
Abstract
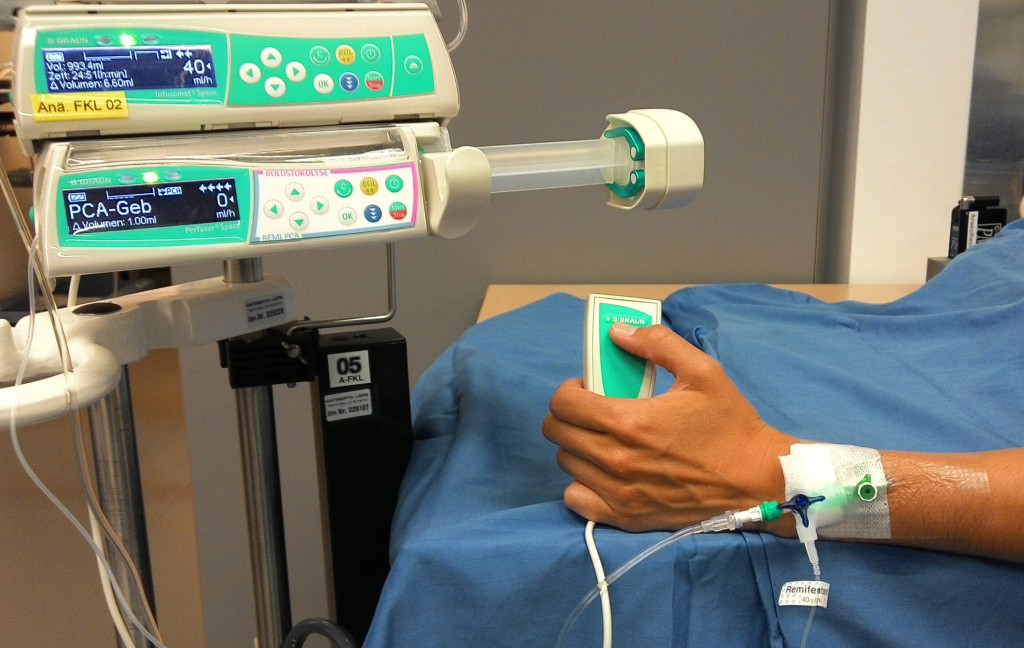
Postoperative pain therapy in patients with myasthenia gravis is difficult due to various drug interactions. Bolusopioid applications can influence muscle tone to varying degrees. Peripheral anesthetics can alter neuromuscular transmission through interaction. Regional anesthesia (PDA) has an unfavorable risk-benefit ratio in thoracoscopic surgery. Opioids with well-controlled pharmacokinetics may therefore be beneficial for pain therapy in patients with myasthenia gravis.
Published
2022-02-12 — Updated on 2025-01-29
How to Cite
Schedler, O., Werner, J., & Grebe, D. (2025). Remifentanil for postoperative analgesia in patients with myasthenia gravis after video-assisted thoracoscopic thymectomy.: DOI: 10.36210/BerMedJ/epub2222022. Berlin Medical Journal, 4(1). Retrieved from https://www.bmjs.me/index.php/BMJ/article/view/38
Issue
Section
original
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Olaf Schedler; Jörg Werner, Dirk Grebe

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




